Water, the vital ingredient of life, is under constant threat due to increasing levels of pollution. The technology to combat this emergent issue is evolving rapidly, with new methods of purifying and treating water being developed continually. One such groundbreaking innovation is the 'Multimedia Filter', an instrument that holds immense potential in dealing with numerous water treatment challenges.
Multimedia filters leverage a process wherein one or several filter media help pass high-turbidity water through a certain thickness of granular or non-granular material under specific pressure. The goal? To effectively eliminate suspended chromatin and clarify water. The filter media can range from quartz sand to anthracite and manganese sand. These filters are primarily deployed for water treatment and degreasing, softened water and pre-treatment of pure water. The end result is a remarkably lower effluent turbidity, reaching below three degrees.

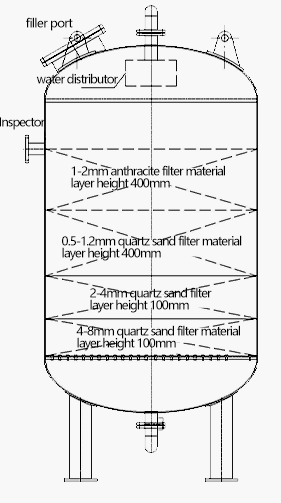
Structure of Multimedia Filters
The core components of multimedia filters include a tank body, water distribution and collection systems, a filter material layer, a partition (plate) water cap, a supporting layer and internal supporting pipelines. The key pipeline and its matching control valve, pressure gauge, and sampling valve are also part of the structure.
One distinguishing feature of multimedia filters is the use of quartz sand and anthracite as filter materials for pressure filtration. The advantages of this filtration method include a large filtration area and a vast amount treated water leading to highly cost-effective packing operations.
Applications and Advantages
Multimedia filters find extensive use in multiple sectors including cooling water treatment, raw water treatment for paper and food processing industries, industrial circulating water, electric sewage, and urban tap water, all thanks to their distinct features.
The filter material used is not only corrosion-resistant but also highly porous, offering the largest dirt-carrying capacity. It's moderate density makes it easy to backwash. In addition, the filter's primary material, which can range from Stainless steel 304, Stainless steel 316, to Q235 carbon steel, ensures a broad water treatment capacity of 0.5~200T/h per unit.
One of the major advantages of using multimedia filters is their excellent interception ability that results in minimized water loss and excellent filtration effect. This, in turn, removes impurities such as mud, suspended solids, colloids, and algae in water, reducing mechanical damage to a significant extent.
Multimedia filters are bookmarked for their simple structure, making them easy to operate and maintain. They are known for their high pollution capacity and are easy to clean. Moreover, they can be customized according to the actual working conditions, ensuring an applicable and functional solution for water treatment.
The Multimedia Filter Paradigm
The working principle of multimedia filters revolves around a mechanical filter based on a bed of layered anthracite, sand, finely divided garnet or other materials. In essence, it is a process of depth filtration, wherein the larger particles in the water are removed in the top layer, and the smaller particles are diligently removed in the deeper layers of the filter medium.
As a result, the water quality reaches a standard after coarse filtration. When raw water passes through the filter material, the suspended solids in the water are entrapped due to adsorption and mechanical resistance.
This technology is pressure-enabled and designed in such a way that when the water flows into the middle of the filter layer, the sand particles in the water adhere closely to provide more opportunities for the particles in the water to collide with the sand particles. In this way, the flocs, suspended solids, and the sand particles' surface adhere to each other in water, trapping the impurities within the filter material layer and emanating clarified water quality.
Conclusion
As the challenges of ensuring clean water become ever more complex, the significance and functionality of multimedia filters continue to rise. Whether deployed in power generation, chemical, papermaking, beverages or countless other industries, the multimedia filter is steadily securing its place as an essential tool in securing and treating water.
Versatile, robust, and reliable, these filters not only offer unparalleled convenience but also significantly reduce mechanical damage and ensure safe, clean water for a plethora of uses. A shining beacon of technological progress, the multimedia filter promises cleaner water and thus, a healthier future.
Multimedia filters are a critical part of water treatment systems, tasked with reducing water loss and minimizing the presence of impurities. They execute this crucial role in the following ways:
Interception Ability: Multimedia filters have an excellent interception ability. They hold back and capture more significant particulate matter and debris when water passes through, thus reducing water loss.
Layered Filtration: Multimedia filters use multiple layers of different materials, with each layer intended to trap different types and sizes of particles. This design ensures a much more thorough filtration process, effectively reducing impurities in the water.
Depth Filtration: Multimedia filters work based on the principle of depth filtration – larger particles are removed in the top layer, medium-sized particles in the middle layer, and tiny particles in the bottom layer. This hierarchal system ensures that impurities are trapped throughout the filter medium, not just on the surface.
Backwashing: The backwashing process employed in multimedia filters helps to clean and reset the filter material. The controlled reversal of water flow dislodges the trapped particles within the filter media, flushing them out of the system and ensuring the filter material can continue to perform optimally. This process is efficient and results in minimal water loss.
Use of Appropriate Filter Media: The choice of filter media (like anthracite, sand, garnet) plays a crucial role in the effectiveness of a multimedia filter. These media have specific properties that make them efficient at trapping particulates without impeding water flow, hence minimizing water loss.
Effective Removal of Suspended Solid Impurities: Multimedia filters are designed to remove suspended solids, colloids, and organic matter from water. By targeting these impurities, multimedia filters contribute to cleaner, safer water.
In a nutshell, the sophisticated design and operation of multimedia filters make them highly effective at minimizing impurities and reducing water loss. From the interception ability to depth filtration, the use of appropriate filter media, and the employment of the backwashing process - every aspect of a multimedia filter is designed to prevent impurities while reducing water loss, ensuring reliable and clean water supply.
Multimedia filters use several layers of filtering material, each with a distinct purpose in the purification process. These layers are carefully structured from coarse at the top to fine at the bottom, allowing the filter to trap particles of descending sizes and achieve higher efficiency. Here is a rundown of the common layers used in multimedia filters.
Anthracite: This is generally the topmost layer, which is coarse and light. It is effective in removing larger particles due to its larger grain size, reducing the load on the following layers. In addition, Anthracite has a high dirt-holding capacity, meaning it can filter more sediment before needing to be backwashed.
Sand: Located beneath the layer of anthracite, the sand layer is designed to filter out smaller particles that pass through the anthracite layer. Its primary function is to reduce turbidity by trapping fine suspended solids.
Garnet: This layer typically lies beneath the sand layer. Garnet has a denser and smaller grain size, enabling it to capture smaller impurities that passed through the sand and anthracite layers.
Gravel: Lying at the bottom, the gravel layer serves as a support base for the above layers, preventing them from entering the water distribution system during backwashing. Also, due to its larger grain size, the gravel layer promotes better water flow and distribution throughout the filter.
Each of these layers contributes to efficient filtration. Larger impurities are trapped in the upper anthracite layer while smaller particles are caught by the finely granulated garnet layer. Through this layered structure, multimedia filters drastically enhance the water's quality by significantly reducing impurities.
When it comes to backwashing, the layers unmix due to their distinct densities, ensuring efficient removal of the retained impurities. Once the backwashing process is completed, the layers return to their original places, prepared for another round of filtration. This structured, efficient operation makes multimedia filters an excellent choice for water purification.
The anthracite layer plays an essential role in the filtration process in multimedia filters. Situated as the uppermost layer in the filter, it comprises a coarse but lightweight material that's denser than water yet lighter than the underlying sand and garnet layers.
Trapping Large Particles: The larger grain size of anthracite makes it suited for intercepting and retaining larger suspended particles and impurities present in the water. By capturing these large particles, the anthracite layer reduces the load on subsequent filter layers and improves the overall efficiency of the filtration process.
Prolonging Filter Life: As it captures larger particles, the anthracite layer protects the layers underneath it from rapid clogging, extending the overall lifespan of the filter and reducing the frequency of backwashing.
Preventing Loss of Filter Media: During the backwash cycle, the anthracite layer rises above the other layers due to its lower density, allowing the trapped impurities to be efficiently flushed out. This prevents the loss of filter media during backwash, maintaining the filter's performance over time.
Promoting Even Water Distribution: The relatively larger grain sizes of the anthracite layer also contribute to even water flow during the filtration process as water enters the filter. This ensures that the entire cross-section of the filter is used, optimizing both the efficiency and effectiveness of the filtration process.
In essence, the anthracite layer in multimedia filters stands as the first line of defense against impurities, promoting efficient, long-lasting operation of the entire filtration system.









